Haemodialysis
September 8, 2020 | by Yashaswi Pathakamuri | Posted in Diseases, Nutrition Facts
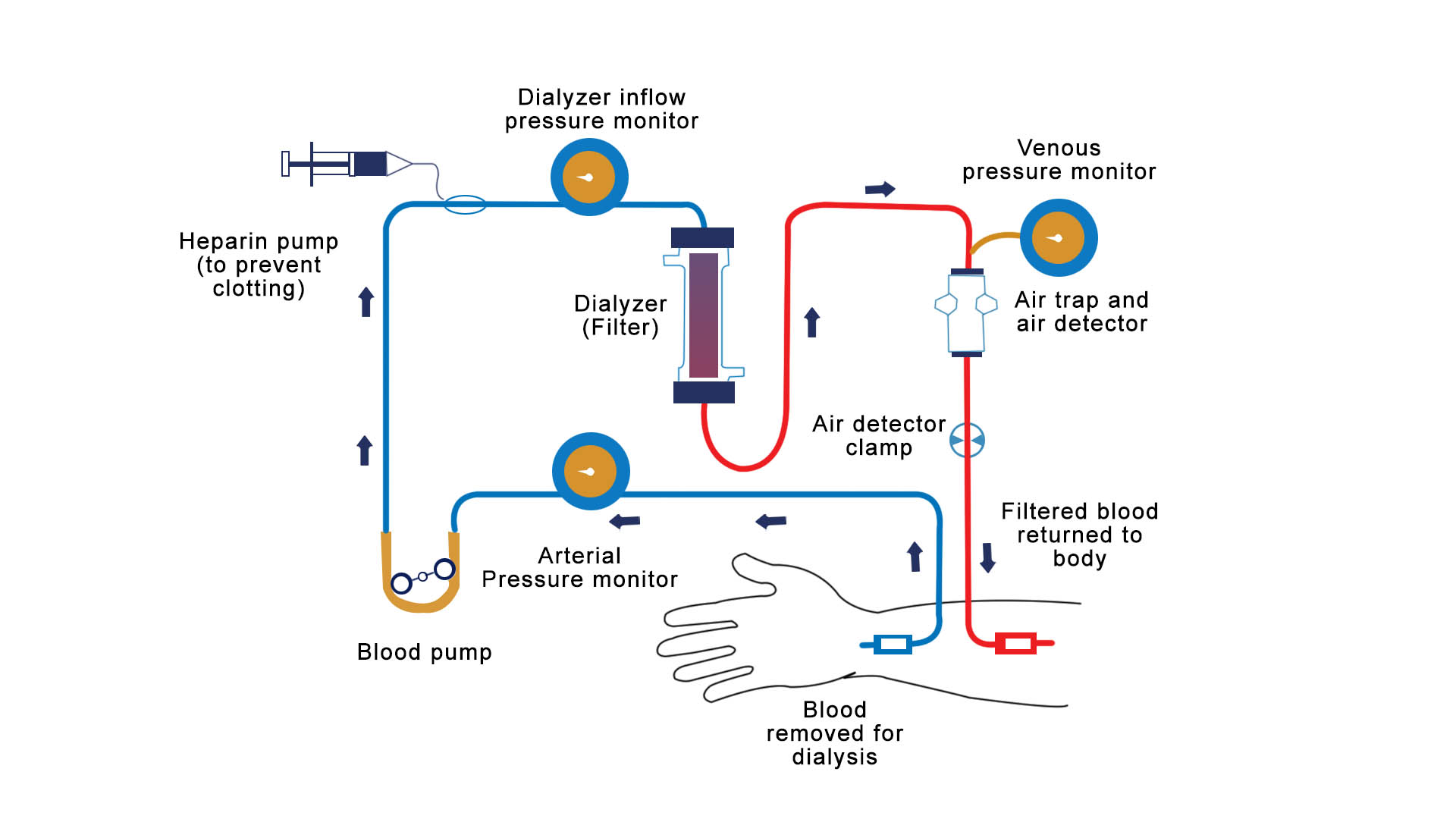
Hemodialysis is a treatment to filter wastes and water from your blood, as your kidneys did when they were healthy. Hemodialysis helps control blood pressure and balance important minerals, such as potassium, sodium, and calcium, in your blood.
In haemodialysis, an artificial kidney, haemodialysis is used to remove the waste products from the blood and restore the body’s chemical balance.
Hemodialysis can help you feel better and live longer, but it’s not a cure for kidney failure.
What is haemodialysis?
Haemodialysis is the most common type of dialysis and the one most people are aware of. During the procedure, a tube is attached to a needle in your arm. Blood passes along the tube and into an external machine that filters it, before it’s passed back into the arm along another tube.
In hemodialysis, blood is removed from the body and filtered through a man-made membrane called a dialyzer, or artificial kidney, and then the filtered blood is returned to the body. The average person has about 10 to 12 pints of blood during dialysis only one pint (about two cups) is outside of the body at a time. Blood passes along the tube and into an external machine that filters it, before it’s passed back into the arm along another tube.
When should i go for haemodialysis?
If you had sudden acute kidney injury, you may need hemodialysis only for a short time until your kidneys recover. You need dialysis when you develop end stage kidney failure, usually by the time you lose about 85 to 90 percent of your kidney function and have a GFR of <15.
Also know about:
Dietary management for acute kidney failure.
Haemodialysis means you’ll have 4 treatment-free days a week, but the treatment sessions last longer and you may need to visit hospital each time.
How is haemodialysis done?
A blood vessel with a rapid flow of blood that is also close to the skin is needed for haemodialysis. This doesn’t exist naturally which is why an access has to be made. It is made during a short surgery using one of the two methods as shown below:
A fistula is made by connecting a vein to a nearby artery. Blood flows rapidly into the vein making it larger. It takes weeks to months before a fistula is ready for use.
A graft may be sewn between the artery and vein. Blood flows rapidly through the graft from the artery to vein. A graft is usually ready to be used during treatment after a week or two.
Can haemodialysis done at home?
Yes!! in home haemodialysis, you’ll usually be recommended to have dialysis sessions more often than you would in a clinic, but you can choose a treatment plan that meets your medical needs and fits around your life.
It can also be done at home. Some examples of a home dialysis include:
- 4 times a week for 4 hours
- 5 times a week for 3 hours
- 6 days a week for 8 hours overnight
Recent Posts
Categories
- Arthritis
- B vitamins
- Berries
- Best time to take
- Breasfeeding
- cancer
- Chronic Diseases
- COVID-19
- Dairy
- Deficiency
- Diabetes
- Diet
- Diseases
- FAQ's
- Fats
- Fever
- Hair
- health
- Kidney
- Leafy Vegetables
- Lung disease
- mango
- Meat
- Millets
- Minerals
- Myositis
- Nausea
- Nutrition Facts
- Nuts and Seeds
- Oats and Oatmeal
- Psoriasis
- Recipes
- Rice
- Skin
- spices and Condiments
- Summer
- Thyroid
- Varicose Veins
- Vegetables
- Vitamins
- Vomiting
- water
- weight gain
- weight Loss
Archives
- April 2024
- March 2024
- February 2024
- January 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- October 2023
- September 2023
- August 2023
- July 2023
- June 2023
- May 2023
- April 2023
- March 2023
- February 2023
- January 2023
- November 2022
- October 2022
- September 2022
- August 2022
- July 2022
- June 2022
- May 2022
- April 2022
- March 2022
- February 2022
- January 2022
- December 2021
- November 2021
- October 2021
- September 2021
- July 2021
- June 2021
- May 2021
- April 2021
- March 2021
- February 2021
- January 2021
- December 2020
- November 2020
- October 2020
- September 2020
- August 2020
- July 2020
- June 2020
- May 2020
- April 2020
- March 2020
- February 2020
- January 2020