Phenylketonuria (PKU) – Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis
August 27, 2020 | by Sravani Pathakamuri | Posted in Nutrition Facts
Phenylketonuria (PKU) is a rare inherited metabolic disease, which can lead to severe brain disorder caused by an amino acid accumulation, i.e, phenylalanine to the toxic levels in the blood and the brain. Though it is an autosomal recessive disorder, it pass down through the families to the baby.
or
PKU is said to be a rare inherited disorder or inborn error metabolism of amino acid phenylalanine. This cause phenylalanine buildup in the body, this happens because PKU affected person had a defect in the gene itself which helps to create the enzyme that break down phenylalanine.
When PKU patient takes protein rich foods or aspartame – an artificial sweetener. a dangerous buildup of phenylketonuria takes place. It is because phenylketonuria patient lack the enzyme that break down phenylalanine. As we all know that amino acids are the building blocks of protein, like that phenylalanine is one of the essential amino acids, which is necessary for our life. But our body cannot made it, so we obtain this from protein rich foods like egg, meat, chicken. cheese, milk whole grains etc.
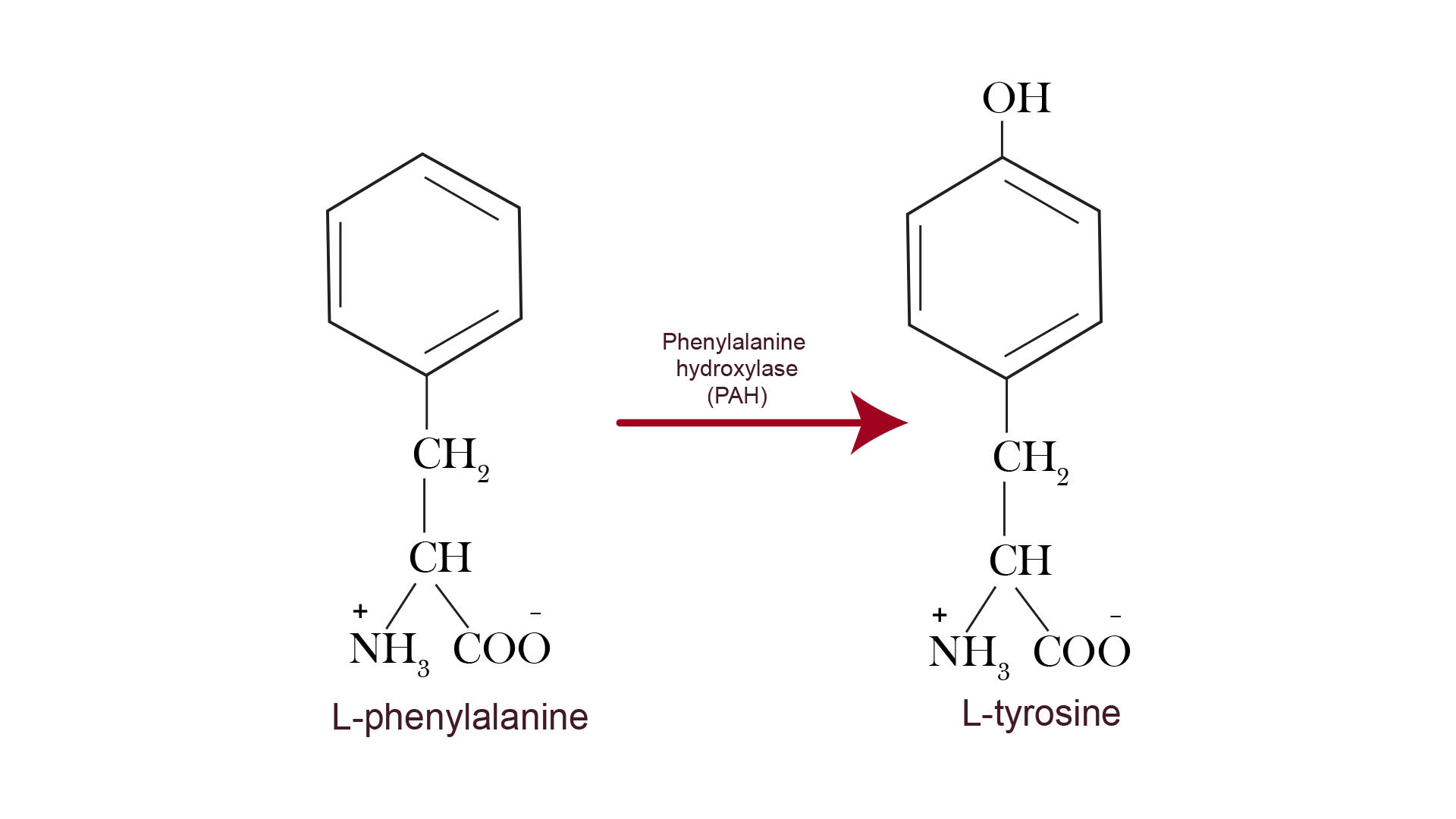
Generally, phenylalanine after entering into the body converts into tyrosine by the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase. After that tyrosine is converted into neurotransmitter which is important for brain functions and development.
Phenylalanine plays a role in the body’s production of melanin, the pigment which is responsible for skin and hair colour.
Causes Of PKU
Generally, PKU is an autosomal recessive disorder caused by insufficient PAH. Phenylketonuria, it is caused by impaired activity of liver enzyme, phenylalanine hydroxylase which oxidises phenylalanine to tyrosine. Some other types of phenylketonuria caused by the defects in the synthesis of tetrahydrobiopterin. A dangerous buildup of phenylalanine can occur when someone eats high-protein foods, such as meat.
Phenylketonuria is inherited, which passes down through families. Both parents must pass on the a nonworking copy of the gene in order for a baby to have the condition.
Symptoms
- Motor Irritability
- Hyperactivity
- Convulsive Seizures
- Strange Behaviour
- Psychiatric Disorders
- Intellectual Disability
- Delayed Development
- A Musty Odor In The Breath, Skin & Urine
- Psychiatric Disorders
- Microcephaly
- Jerking movements of the arms and legs
Untreated PKU in children generally develop some symptoms due to lack of melanin production in the body as following:
- Light Brown Hair
- Blue Eyes
- Fair Skin which may cause Eczema
The disease is generally expressed at 3 to 6 months of age. and is characterised by all the above symptoms. If not treated before 3 weeks of age, the metabolic imbalance produces irreversible mental retardation. Ihe IQ levels of affected persons is usually below 50. Central nervous system is also damaged by causing above symptoms. Because tyrosine is normally produced from phenylalanine which is useful in the production of the pigment melanin.
Diagnosis
Since many year, PKU is diagnosed by taking blood sample. Screening test the most common test performed for PKU diagnosis, newborns with blood phenylalanine concentration greater than 2 mg/ dl on the screening test is restudied.
Guthrie test is a routine blood test carried out on babies a few days after birth to detect the condition phenylketonuria. A doctor uses a needle or lancet to take a few drops of blood from your baby’s heel to test for PKU.
If the initial screening test is greater than 8 mg/dl plasma amino acids should be quantitated by ion exchange chromatography with the infant on a known phenylalanine intake form natural protein sources.
Further tests are done to confirm the initial results. These tests are often done within six weeks after birth. All these tests are done to know the presence of the PAH gene mutation that causes PKU.
Summary
If the both parents are PKU patients, their child may also inherit this disorder. If one the parent is PKU positive, there’s a 50 – 50 chance to the child and symptoms are also not shown in some cases. PKU is can be prevented and treated by modifying the patients daily diet with low or restricted protein foods.
Treatment, prevention and dietary modifications are to be posted in the next article in detailed.