Acute Renal Failure: Causes And Symptoms
July 10, 2020 | by Yashaswi Pathakamuri | Posted in Kidney
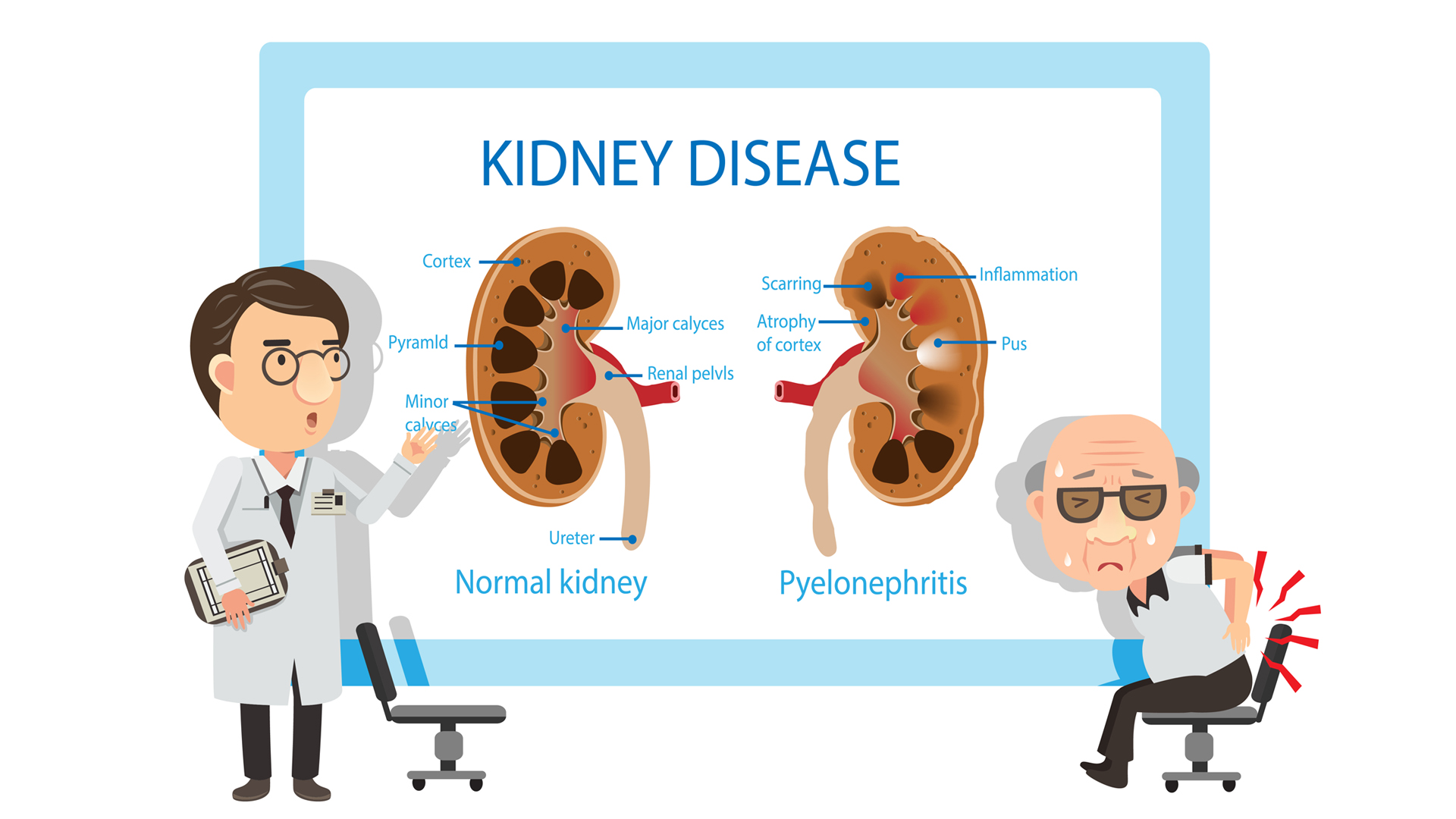
Acute renal failure occurs when your kidneys suddenly become unable to filter waste products from your blood. When your kidneys lose their filtering ability, dangerous levels of wastes may accumulate, and your blood’s chemical makeup may get out of balance. This article tells you about the causes and symptoms of acute renal failure.
Acute renal failure is most common in people who are already hospitalized, particularly in critically ill people who need intensive care. Acute kidney failure can be fatal and requires intensive treatment. Anyway, acute kidney failure may be reversible.
There is a sudden shutdown of renal function following metabolic insult or traumatic injury to normal kidneys. There is high mortality and the condition needs a medical emergency in which the nutritionist plays supporting role.
Causes
Acute kidney failure can occur when:
- Loss of blood can cause acute renal failure, as there is blood flow to kidney decreases as in accidents, ulcers, internal hemorrhage or at the time of delivery.
- Loss of fluid in diarrhea, vomiting, diabetic coma (excessive urination and excessive sweating).
- Loss of plasma as in burns and injuries.
- Nephritis or nephrosis can also result in acute renal failure.
- Nephrotoxins like paracetamol and mushrooms.
- General Anesthesia and surgical operation reduce renal blood flow and may precipitate renal failure.
- Acute haemolytic disorders (RBC are destroyed due to some diseases).
- Serious infections produce shock and reduce renal blood.
Symptoms
Symptoms and signs of acute kidney failure may include:
- Low urine volume (anuria or oliguria).
- Accumulation of waste products of protein metabolism in blood. serum urea nitrogen and creatinine levels are increased.
- Excretion of potassium is diminished. The rise in potassium is due to its release from tissue protein during breakdown to provide calories.
- The urinary output may be as little as 20 to 200 ml/day.
- Chest pain or pressure
- Seizures or coma in severe cases
- There is also increased phosphate and sulphate with decreased sodium, calcium and base bicarbonate.
- The patient may be lethargic, anorexia and suffer from nausea and vomitings. There may be elevation of blood pressure and signs of ureamia.
- Oral intake is difficult during this period.
- Fluid retention, causing swelling in your legs, ankles or feet
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Confusion
- Weakness
- Irregular heartbeat
- Death is caused not because of rise in blood urea, but potassium intoxication or water intoxication due to over treatment with fluids to stimulate urine excretion.
Sometimes acute kidney failure causes no signs or symptoms and is detected through lab tests done for another reason.
Recent Posts
Categories
- Arthritis
- B vitamins
- Berries
- Best time to take
- Breasfeeding
- cancer
- Chronic Diseases
- COVID-19
- Dairy
- Deficiency
- Diabetes
- Diet
- Diseases
- FAQ's
- Fats
- Fever
- Hair
- health
- Kidney
- Leafy Vegetables
- Lung disease
- mango
- Meat
- Millets
- Minerals
- Myositis
- Nausea
- Nutrition Facts
- Nuts and Seeds
- Oats and Oatmeal
- Psoriasis
- Recipes
- Rice
- Skin
- spices and Condiments
- Summer
- Thyroid
- Varicose Veins
- Vegetables
- Vitamins
- Vomiting
- water
- weight gain
- weight Loss
Archives
- April 2024
- March 2024
- February 2024
- January 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- October 2023
- September 2023
- August 2023
- July 2023
- June 2023
- May 2023
- April 2023
- March 2023
- February 2023
- January 2023
- November 2022
- October 2022
- September 2022
- August 2022
- July 2022
- June 2022
- May 2022
- April 2022
- March 2022
- February 2022
- January 2022
- December 2021
- November 2021
- October 2021
- September 2021
- July 2021
- June 2021
- May 2021
- April 2021
- March 2021
- February 2021
- January 2021
- December 2020
- November 2020
- October 2020
- September 2020
- August 2020
- July 2020
- June 2020
- May 2020
- April 2020
- March 2020
- February 2020
- January 2020